Probably, you’ve heard that the
Internet of Things has the power to drastically change our lives, from how we
manage and operate our homes to even automating jobs across nearly all
industries. But what is IoT actually? I’ve been asked that question more times
than I can count and, over the past several years, I’ve boiled the answer down
to something that I think anyone can understand. In this article, I’m going to
share everything you need to know about the Internet of Things.
🌟 Definition:
 “The Internet of Things (IoT) is a
system of interrelated computing devices, mechanical and digital machines,
objects, animals or people that are provided with unique identifiers and the
ability to transfer data over a network without requiring human-to-human or
human-to-computer interaction.”
“The Internet of Things (IoT) is a
system of interrelated computing devices, mechanical and digital machines,
objects, animals or people that are provided with unique identifiers and the
ability to transfer data over a network without requiring human-to-human or
human-to-computer interaction.”🌟 What is IoT ?
The Internet of Things is actually a pretty simple concept, it means taking all the things in the world and connecting them to the internet.
Internet of Things(IoT) is a network of physical objects or people called "things" that are embedded with software, electronics, network, and sensors that allows these objects to collect and exchange data. The goal of IoT is to extend to internet connectivity from standard devices like computer, mobile, tablet to relatively dumb devices like a toaster.
🌟 How IoT works:

An IoT ecosystem consists of web-enabled smart devices that use embedded systems, such as processors, sensors and communication hardware, to collect, send and act on data they acquire from their environments. IoT devices share the sensor data they collect by connecting to an IoT gateway or other edge device where data is either sent to the cloud to be analyzed or analyzed locally.
Sometimes, these devices communicate with other related devices and act on the information they get from one another. The devices do most of the work without human intervention, although people can interact with the devices -- for instance, to set them up, give them instructions or access the data.
The connectivity, networking and communication protocols used with these web-enabled devices largely depend on the specific IoT applications deployed.
IoT can also make use of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning to aid in making data collecting processes easier and more dynamic.
Here, are four fundamental components of an IoT system:
1) Sensors/Devices: Sensors or devices are a key component
that helps you to collect live data from the surrounding environment. All this
data may have various levels of complexities. It could be a simple temperature
monitoring sensor, or it may be in the form of the video feed.
A device may have various types of sensors which performs multiple tasks apart from sensing. Example, A mobile phone is a device which has multiple sensors like GPS, camera but your smartphone is not able to sense these things.
2) Connectivity: All the collected data is sent to a cloud infrastructure. The sensors should be connected to the cloud using various mediums of communications. These communication mediums include mobile or satellite networks, Bluetooth, WI-FI, WAN, etc.
3) Data Processing: Once that data is collected, and it gets to the cloud, the software performs processing on the gathered data. This process can be just checking the temperature, reading on devices like AC or heaters. However, it can sometimes also be very complex like identifying objects, using computer vision on video.
4)User Interface: The information needs to be available to the end-user in some way which can be achieved by triggering alarms on their phones or sending them notification through email or text message. The user sometimes might need an interface which actively checks their IOT system. For example, the user has a camera installed in his home. He wants to access video recording and all the feeds with the help of a web server.
For example, if a user detects any changes in the temperature of the refrigerator, with the help of IOT technology the user should able to adjust the temperature with the help of their mobile phone
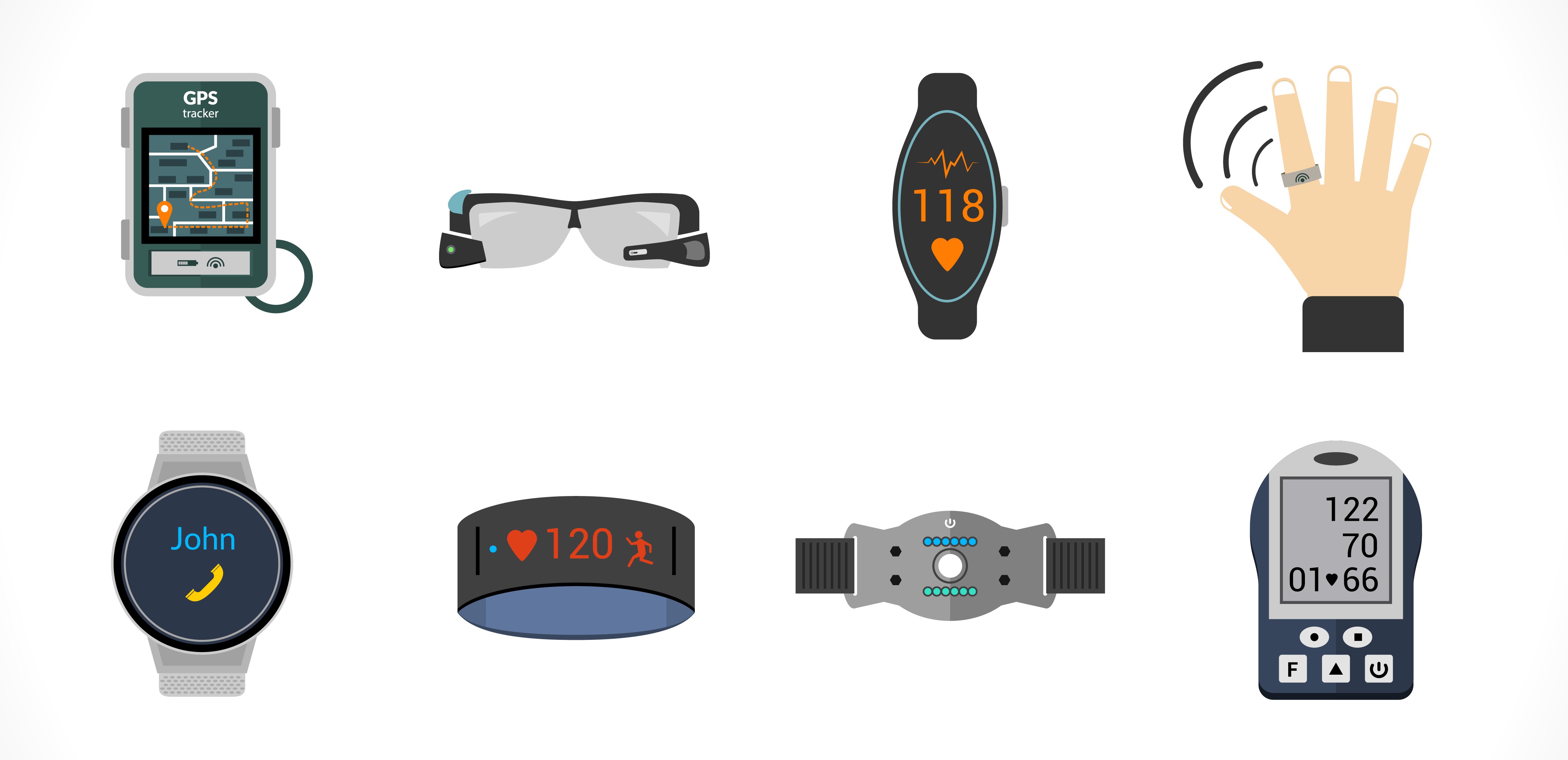 Wearable technology is a hallmark of IoT
applications and probably is one of the earliest industries to have deployed
the IoT at its service. We happen to see Fit Bits, heart rate monitors and
smartwatches everywhere these days.
Wearable technology is a hallmark of IoT
applications and probably is one of the earliest industries to have deployed
the IoT at its service. We happen to see Fit Bits, heart rate monitors and
smartwatches everywhere these days.
A device may have various types of sensors which performs multiple tasks apart from sensing. Example, A mobile phone is a device which has multiple sensors like GPS, camera but your smartphone is not able to sense these things.
2) Connectivity: All the collected data is sent to a cloud infrastructure. The sensors should be connected to the cloud using various mediums of communications. These communication mediums include mobile or satellite networks, Bluetooth, WI-FI, WAN, etc.
3) Data Processing: Once that data is collected, and it gets to the cloud, the software performs processing on the gathered data. This process can be just checking the temperature, reading on devices like AC or heaters. However, it can sometimes also be very complex like identifying objects, using computer vision on video.
4)User Interface: The information needs to be available to the end-user in some way which can be achieved by triggering alarms on their phones or sending them notification through email or text message. The user sometimes might need an interface which actively checks their IOT system. For example, the user has a camera installed in his home. He wants to access video recording and all the feeds with the help of a web server.
For example, if a user detects any changes in the temperature of the refrigerator, with the help of IOT technology the user should able to adjust the temperature with the help of their mobile phone
🌟 Real World IoT Applications in Different Domains:
1. IoT Applications – Wearables
 Wearable technology is a hallmark of IoT
applications and probably is one of the earliest industries to have deployed
the IoT at its service. We happen to see Fit Bits, heart rate monitors and
smartwatches everywhere these days.
Wearable technology is a hallmark of IoT
applications and probably is one of the earliest industries to have deployed
the IoT at its service. We happen to see Fit Bits, heart rate monitors and
smartwatches everywhere these days.
2. IoT
Applications – Smart Home Applications
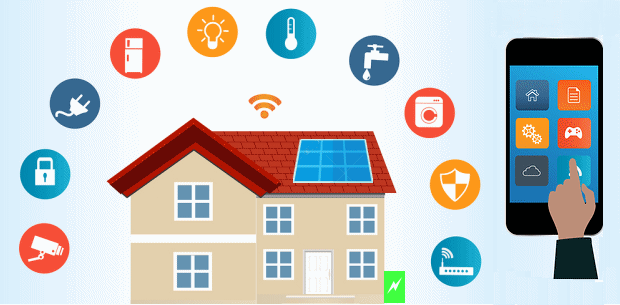 When we talk about IoT Applications, Smart Homes
are probably the first thing that we think of. The best example I can think of
here is Jarvis, the AI home automation employed by Mark
Zuckerberg. There is also Allen Pan’s Home Automation System where functions in
the house are actuated by use of a string of musical notes
When we talk about IoT Applications, Smart Homes
are probably the first thing that we think of. The best example I can think of
here is Jarvis, the AI home automation employed by Mark
Zuckerberg. There is also Allen Pan’s Home Automation System where functions in
the house are actuated by use of a string of musical notes
IoT applications can turn reactive medical-based systems into proactive
wellness-based systems.
 The resources that current medical research uses,
lack critical real-world information. It mostly uses leftover data, controlled
environments, and volunteers for medical examination. IoT opens ways to a sea
of valuable data through analysis, real-time field data, and testing.
The resources that current medical research uses,
lack critical real-world information. It mostly uses leftover data, controlled
environments, and volunteers for medical examination. IoT opens ways to a sea
of valuable data through analysis, real-time field data, and testing.
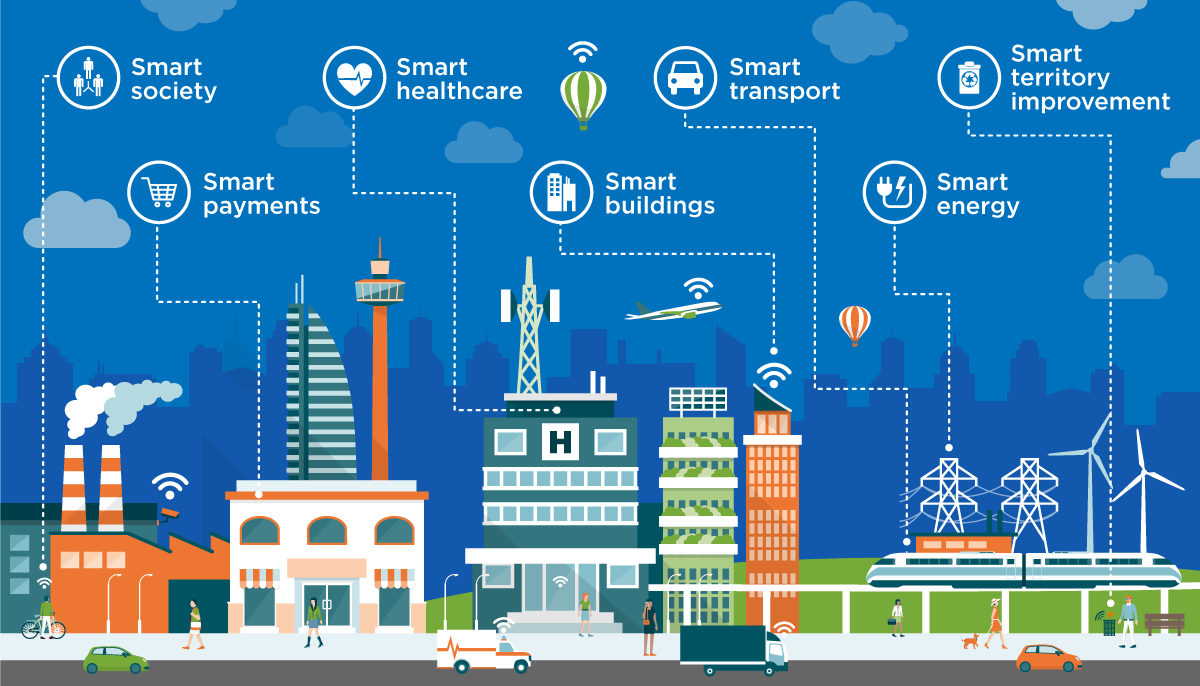 Smart cities, like its name suggests, is a big innovation and spans a wide
variety of use cases, from water distribution and traffic management to waste
management and environmental monitoring. The reason why it is so popular is
that it tries to remove the discomfort and problems of people who live in
cities. IoT solutions offered in the smart city sector solve various
city-related problems, comprising of traffic, reducing air and noise pollution,
and helping to make cities safer
Smart cities, like its name suggests, is a big innovation and spans a wide
variety of use cases, from water distribution and traffic management to waste
management and environmental monitoring. The reason why it is so popular is
that it tries to remove the discomfort and problems of people who live in
cities. IoT solutions offered in the smart city sector solve various
city-related problems, comprising of traffic, reducing air and noise pollution,
and helping to make cities safer
 When we talk about IoT Applications, Smart Homes
are probably the first thing that we think of. The best example I can think of
here is Jarvis, the AI home automation employed by Mark
Zuckerberg. There is also Allen Pan’s Home Automation System where functions in
the house are actuated by use of a string of musical notes
When we talk about IoT Applications, Smart Homes
are probably the first thing that we think of. The best example I can think of
here is Jarvis, the AI home automation employed by Mark
Zuckerberg. There is also Allen Pan’s Home Automation System where functions in
the house are actuated by use of a string of musical notes
3. IoT Applications – Health Care
 The resources that current medical research uses,
lack critical real-world information. It mostly uses leftover data, controlled
environments, and volunteers for medical examination. IoT opens ways to a sea
of valuable data through analysis, real-time field data, and testing.
The resources that current medical research uses,
lack critical real-world information. It mostly uses leftover data, controlled
environments, and volunteers for medical examination. IoT opens ways to a sea
of valuable data through analysis, real-time field data, and testing.
The Internet of Things also improves the current
devices in power, precision, and availability. IoT focuses on creating
systems rather than just equipment.
4. Smart City
 Smart cities, like its name suggests, is a big innovation and spans a wide
variety of use cases, from water distribution and traffic management to waste
management and environmental monitoring. The reason why it is so popular is
that it tries to remove the discomfort and problems of people who live in
cities. IoT solutions offered in the smart city sector solve various
city-related problems, comprising of traffic, reducing air and noise pollution,
and helping to make cities safer
Smart cities, like its name suggests, is a big innovation and spans a wide
variety of use cases, from water distribution and traffic management to waste
management and environmental monitoring. The reason why it is so popular is
that it tries to remove the discomfort and problems of people who live in
cities. IoT solutions offered in the smart city sector solve various
city-related problems, comprising of traffic, reducing air and noise pollution,
and helping to make cities safer🌟 Internet of Things (IoT): Pros and Cons:
ADVANTAGES 🠊
➤ Automation: Automation
leads to uniformity in tasks, quality of service and control of day-to-day
tasks without human intervention. Machine-to-machine communication also helps
maintain transparency throughout the process
➤ Efficiency: Machine-to-machine
interaction provides for better efficiency, enabling people to focus on other
jobs.
➤ Cost
Savings: In
addition to the optimal utilization of energy and resources, the IoT helps
alleviate the problems associated with bottlenecks, breakdowns and system
damages.
➤ Communication: IoT allows
physical devices to stay connected and better communicate, which creates
greater quality control.
➤ Instant
Data Access: More
available information helps simplify the decision making process, making life
easier to manage.
DISADVANTAGES🠊
➤ Privacy and Security : As many of our everyday appliances, machines and
services become connected to the internet, much more information is readily
available. It makes it harder to keep confidential information out of the hands
of hackers and other unauthorized users
➤ Compatibility: Currently, there is not international standard of compatibility for the IoT which can make it hard for devices from different manufacturers to communicate with each other
➤ Complexity: Because the IoT is such a vast, diverse network, a single failure in either the software or hardware can have disastrous consequences.
➤ Less Jobs: As IoT brings in more consistent automation, we could see a decline in the need for unskilled employees in the workplace.
➤ Technologically Dependent Life: As our lives become more and more dependent on technology, basic human interaction skills will be reduced across society.
🌟 QUOTE:
“If you think that the
internet has changed your life, think again. The Internet of Things is about to
change it all over again!”
